Brain activity at rest
When someone is awake but not consciously engaged in any task, whether physical or mental, they are said to be resting. During this state, the individual is conscious and involved in internally directed thought. These spontaneous mental explorations, commonly referred to as 'mind-wandering,' are often centered around typical life events, such as recalling past experiences, analyzing current internal sensations, contemplating problems, or planning for the future. This particular state of mind is of particular interest.
- What relationships exist between resting-state brain activity and cognitive performance?
- Can brain networks in a resting state predict clinical scores?
- Are intrinsic functional networks associated with fundamental differences between individuals, such as in personality?
- How does cognitive rehabilitation impact brain networks during rest?
Neurofeedback therapy
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback that utilizes real-time monitoring of brainwave activity to facilitate self-regulation of brain function. Typically, it entails the placement of sensors on the scalp to gauge the electrical activity in the brain (known as electroencephalography or EEG). This data is subsequently conveyed back to the individual through visual or auditory stimuli, such as sounds or images displayed on a computer screen.
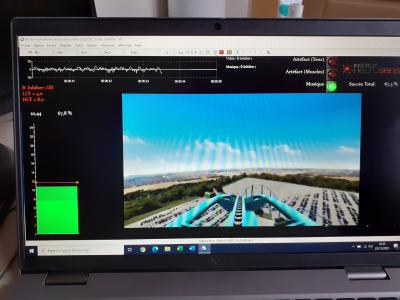
- Could neurofeedback potentially benefit individuals experiencing Subjective Cognitive Decline?
- What factors contribute to more effective learning in neurofeedback?